A Short Guide To Ten Different Types of Skin Diseases (And How To Treat Each One)
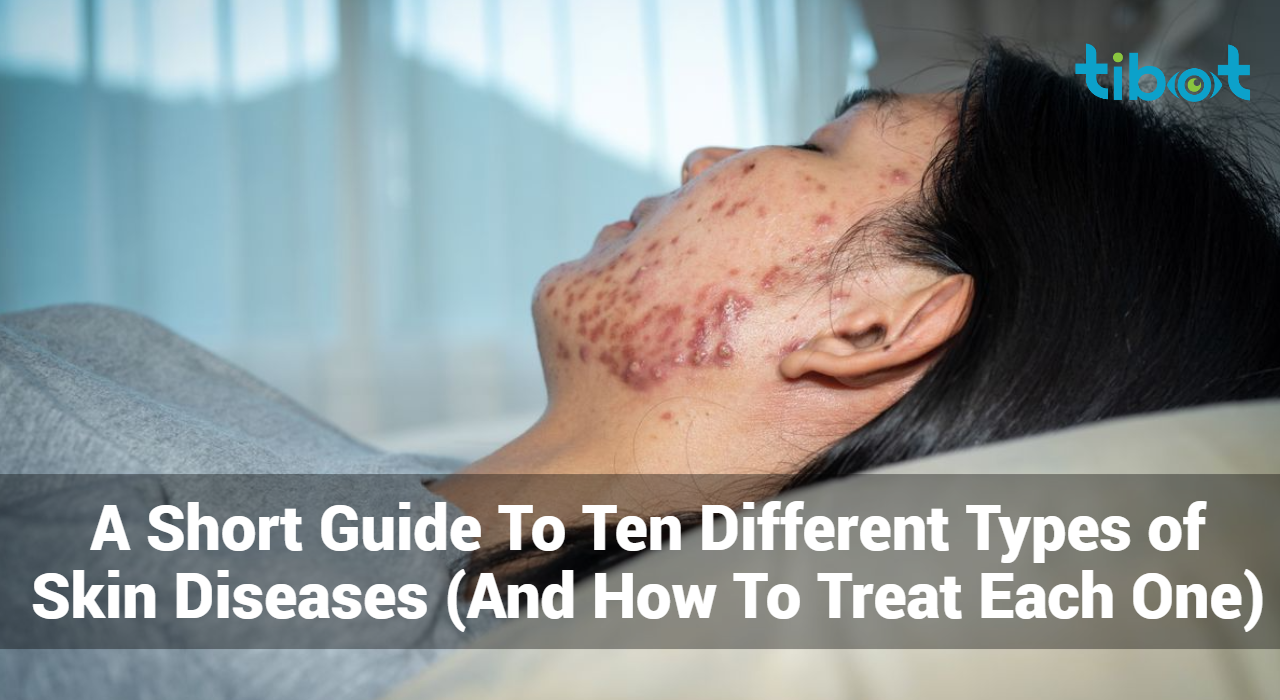
Skin diseases affect millions worldwide, presenting diverse symptoms and requiring tailored treatments. This short guide aims to demystify 10 prevalent skin conditions, offering insights into their causes and effective management strategies.
What is a skin disease?
A skin disease, also known as a dermatological disorder or dermatosis, refers to any medical condition that affects the skin. Skin diseases can manifest in various forms, ranging from mild irritations to chronic, debilitating conditions. These conditions can affect individuals of all ages, genders, and ethnicities and may result from a combination of genetic, environmental, immunological, and lifestyle factors.
Skin diseases can affect different layers of the skin, including the epidermis (outermost layer), dermis (middle layer), and subcutaneous tissue (innermost layer). They can present with a wide range of symptoms, such as redness, itching, swelling, rash, blistering, scaling, and discoloration. Some skin diseases are localized to specific areas of the body, while others may be widespread or systemic, affecting multiple body systems.
Common Ten Different Types of Skin Diseases:
#01. Psoriasis:
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the skin, leading to the rapid buildup of skin cells. This results in thick, red patches covered with silvery scales, which can be itchy and painful. Psoriasis can occur anywhere on the body but commonly affects the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. Treatment options include topical creams, phototherapy, oral medications, and biologic drugs targeting the immune system.
#02. Acne Vulgaris:
Acne vulgaris is a common skin condition characterized by the formation of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, cysts, and nodules. It occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to the growth of bacteria and inflammation. Acne most often affects the face, but it can also appear on the neck, chest, back, and shoulders. Treatment options include topical creams, oral medications, chemical peels, and laser therapy.
#03. Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis):
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It often appears in childhood and can persist into adulthood. Eczema can manifest in various forms, including red patches, scaling, crusting, and oozing lesions. Triggers for eczema can include allergens, irritants, stress, and environmental factors. Treatment typically involves moisturizers, topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, and avoiding triggers.
#04. Ringworm (Dermatophytosis):
Ringworm, despite its name, is not caused by a worm but by a fungal infection. It presents as a red, circular rash with raised edges and healthy-looking skin in the center, resembling a ring. Ringworm can affect any part of the body, including the scalp (tinea capitis), body (tinea corporis), feet (tinea pedis, or athlete’s foot), and groin (tinea cruris, or jock itch). Treatment typically involves antifungal medications, either topical or oral, to eliminate the fungal infection.
#05. Rosacea:
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition characterized by facial redness, flushing, visible blood vessels, and sometimes pimples or bumps. It typically affects the central face and may worsen over time if left untreated. Treatment includes topical medications, oral antibiotics, laser therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
#06. Dermatitis:
Dermatitis refers to inflammation of the skin, which can have various causes such as allergic reactions, irritants, or genetic factors. Symptoms include redness, itching, swelling, and sometimes blisters or oozing lesions. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may involve topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, or moisturizers.
#07. Impetigo:
Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection commonly seen in children. It is characterized by red sores or blisters that rupture and form honey-colored crusts. Impetigo is usually caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria and is treated with topical or oral antibiotics.
#08. Vitiligo:
Vitiligo is a condition in which the skin loses its pigment cells (melanocytes), resulting in white patches or depigmentation. The exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to involve autoimmune factors. Treatment options include topical corticosteroids, phototherapy, depigmentation therapy, or cosmetic camouflage.
#09. Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) Infection:
HSV infection, commonly known as cold sores or fever blisters, is caused by the herpes simplex virus. It presents as small, painful blisters or sores on the lips, mouth, or genital area. Treatment may involve antiviral medications to reduce symptoms and prevent recurrent outbreaks.
#10. Scabies:
Scabies is a contagious skin infestation caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. It leads to intense itching and a characteristic rash with small red bumps, often in the webbing between fingers, wrists, elbows, and other areas. Treatment typically involves topical scabicidal medications applied to the skin.
Skin Diseases Treatment Options
Treatment options for skin diseases vary depending on the specific condition and its severity. Here are some common treatment approaches for different types of skin diseases:
- Topical Medications:
- Many skin diseases, such as eczema, psoriasis, and acne, can be treated with topical medications applied directly to the affected areas. These medications may include corticosteroids, retinoids, antimicrobials, or immunomodulators. Topical treatments help reduce inflammation, control symptoms, and promote healing of the skin.
- Oral Medications:
- In some cases, oral medications may be prescribed to manage skin diseases, especially when topical treatments are not sufficient or when the condition is widespread or severe. Oral antibiotics, antifungals, antivirals, corticosteroids, or immunosuppressants may be used depending on the underlying cause of the skin disease.
- Phototherapy (Light Therapy):
- Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision. It is commonly used to treat conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, vitiligo, and certain types of dermatitis. Phototherapy helps reduce inflammation, suppress immune responses, and promote skin healing.
- Systemic Treatments:
- Systemic treatments, including biologic drugs and other systemic immunomodulators, are used for severe or refractory skin diseases that do not respond well to topical or oral medications. These medications work by targeting specific components of the immune system involved in the development of skin diseases.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Lifestyle changes can play a crucial role in managing skin diseases and preventing flare-ups. This may include avoiding known triggers such as allergens, irritants, stress, or certain foods. Adopting a gentle skincare routine, maintaining good hygiene practices, protecting the skin from environmental factors (e.g., sun exposure), and managing stress levels can also help improve skin health.
- Surgical Procedures:
- In some cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to treat or manage skin diseases. This may involve procedures such as excision of skin lesions, drainage of abscesses or cysts, laser therapy, cryotherapy (freezing), or skin grafting for severe cases of skin damage or scarring.
- Alternative Therapies:
- Some individuals may explore alternative or complementary therapies for managing skin diseases, such as herbal remedies, acupuncture, acupressure, or dietary supplements. While these therapies may provide relief for some people, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional before trying any alternative treatments to ensure safety and efficacy.
It’s important to note that treatment decisions should be made in consultation with a dermatologist or healthcare professional who can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual needs, medical history, and the specific characteristics of the skin disease.
Conclusion:
Understanding common skin diseases and their treatments empowers individuals to manage symptoms effectively and improve their skin health. While this guide provides general information, consulting a dermatologist for personalized diagnosis and treatment recommendations is crucial for optimal care.
Analyze Skin Diseases
Use our AI chatbot to determine your skin condition