Oral thrush in adults: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Oral thrush, also known as oral candidiasis, is a fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of Candida species, particularly Candida albicans. While often associated with infants, oral thrush can also affect adults, leading to discomfort and potential complications. This comprehensive guide will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for oral thrush in adults, providing an in-depth understanding of this condition.
What is Oral Thrush?
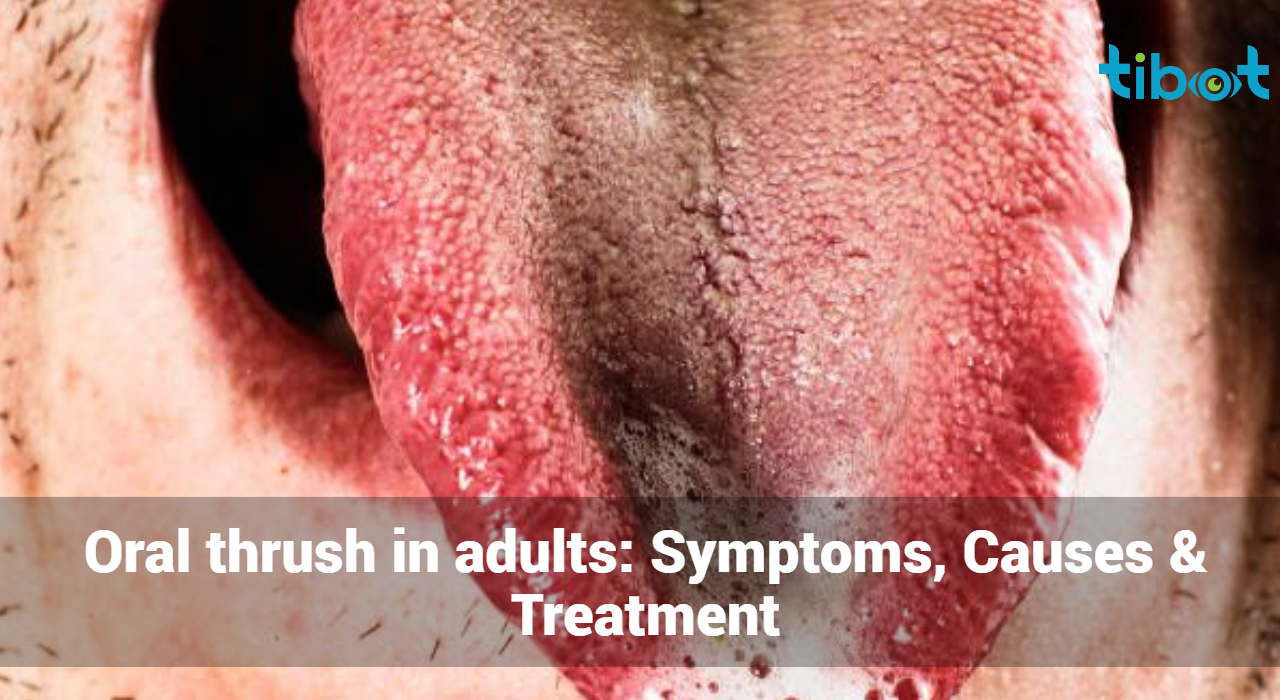
Oral thrush is a condition where a fungal infection develops on the mucous membranes of the mouth, throat, and tongue. The infection is characterized by the growth of Candida fungi, which are normally present in the mouth but can overgrow under certain conditions. This overgrowth leads to the development of white or creamy lesions on the tongue, inner cheeks, gums, and sometimes the roof of the mouth and throat.
What Are The Symptoms of Oral Thrush in Adults?
The symptoms of oral thrush can vary in severity and may include:
- White or Creamy Lesions: These are often the most noticeable symptoms, appearing on the tongue, inner cheeks, gums, and sometimes the roof of the mouth. The lesions may resemble cottage cheese and can be painful or sensitive.
- Redness and Soreness: The affected areas may become red and sore, causing discomfort during eating or swallowing.
- Cracking and Bleeding: The corners of the mouth (angular cheilitis) may crack or bleed, especially if the infection is severe or left untreated.
- Dry Mouth: A persistent dry mouth or feeling of cotton in the mouth may accompany oral thrush.
- Loss of Taste: Some individuals may experience a loss of taste or a persistent bad taste in the mouth.
- Difficulty Swallowing: In more severe cases, oral thrush can cause difficulty swallowing or pain while swallowing.
- Bad Breath: Halitosis or bad breath may develop as a result of the fungal infection.
What Causes of Oral Thrush in Adults?
Several factors can contribute to the development of oral thrush in adults:
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions that compromise the immune system, such as HIV/AIDS, cancer treatments, or immunosuppressive medications, increase the risk of developing oral thrush.
- Diabetes: Poorly controlled diabetes can lead to high blood sugar levels, creating an environment conducive to Candida overgrowth.
- Antibiotic Use: Broad-spectrum antibiotics can disrupt the normal balance of microorganisms in the mouth, allowing Candida to flourish.
- Corticosteroid Use: Inhaled corticosteroids used for conditions like asthma can also disrupt the natural balance of oral flora, increasing the risk of oral thrush.
- Dentures: Poorly fitting dentures or lack of proper denture hygiene can create an environment where Candida thrives.
- Smoking: Tobacco use can contribute to oral thrush by irritating the mucous membranes and altering the oral environment.
- Dry Mouth: Conditions that lead to dry mouth, such as Sjögren’s syndrome or certain medications, can increase the risk of oral thrush.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Deficiencies in essential nutrients, such as vitamin B12 or iron, can also contribute to the development of oral thrush.
Diagnosis of Oral Thrush
Diagnosing oral thrush typically involves:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will review your medical history and perform a physical examination of your mouth and throat.
- Visual Inspection: The characteristic white or creamy lesions are often sufficient for diagnosis, but a healthcare provider will examine these lesions for their appearance and distribution.
- Microscopic Examination: In some cases, a sample of the lesions may be collected and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of Candida fungi.
- Culture: A culture may be taken from the lesions to identify the specific Candida species and determine its sensitivity to antifungal medications.
- Endoscopy: If there is a suspicion of the infection spreading beyond the mouth, an endoscopic examination of the throat or esophagus may be performed.
Analyze Skin Diseases
Use our AI chatbot to determine your skin condition
What Are The Treatment Options of Oral Thrush?
The treatment of oral thrush typically involves antifungal medications and addressing underlying risk factors. Options include:
Antifungal Medications:
- Topical Antifungals: Medications such as nystatin or clotrimazole are applied directly to the affected areas and are effective for mild to moderate cases.
- Oral Antifungals: For more severe or persistent cases, systemic antifungals like fluconazole or itraconazole may be prescribed. These are taken orally and work throughout the body.
- Lozenges and Rinses: Antifungal lozenges or mouth rinses may also be used to treat oral thrush and reduce symptoms.
Managing Underlying Conditions:
- Diabetes Management: Controlling blood sugar levels through diet, medication, or insulin can help prevent recurrent oral thrush.
- Adjusting Medications: If corticosteroids or antibiotics are contributing to oral thrush, your healthcare provider may adjust your treatment plan.
Improving Oral Hygiene:
- Denture Care: Regular cleaning and proper fit of dentures can help prevent oral thrush in denture wearers.
- Brushing and Flossing: Maintaining good oral hygiene through regular brushing and flossing can help reduce the risk of fungal infections.
Dietary Modifications:
- Reducing Sugar Intake: Limiting dietary sugar can help reduce the growth of Candida.
- Probiotics: Consuming probiotics, such as yogurt or supplements, may help restore the balance of oral flora.
Prevention of Oral Thrush
Preventing oral thrush involves maintaining good oral hygiene and managing risk factors:
- Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth twice daily, floss regularly, and use an antiseptic mouthwash if recommended by your dentist.
- Denture Care: Clean dentures daily with a brush and denture cleaner, and remove them at night.
- Controlling Diabetes: Manage your diabetes effectively to maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
- Avoiding Smoking: Quitting smoking can help reduce the risk of oral thrush and improve overall oral health.
- Managing Medications: If you use inhaled corticosteroids, rinse your mouth with water after use to minimize the risk of oral thrush.
- Regular Check-Ups: Schedule regular dental and medical check-ups to monitor and manage any risk factors that may contribute to oral thrush.
Conclusion
Oral thrush is a common fungal infection that can cause discomfort and complications if left untreated. Its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and prevention. By addressing underlying risk factors, maintaining good oral hygiene, and seeking appropriate medical care, adults can manage and prevent oral thrush, ensuring better oral health and overall well-being. If you experience symptoms of oral thrush or have concerns about your oral health, consult a dermatologist or healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.