Guttate Psoriasis in Adults: Symptoms, Causes & Treatments
Guttate psoriasis is a specific type of psoriasis that primarily affects children and young adults, but it can also manifest in adults. This article delves into the symptoms, causes, and treatments of guttate psoriasis, providing a comprehensive overview for those seeking to understand this condition better.
What is Guttate Psoriasis?
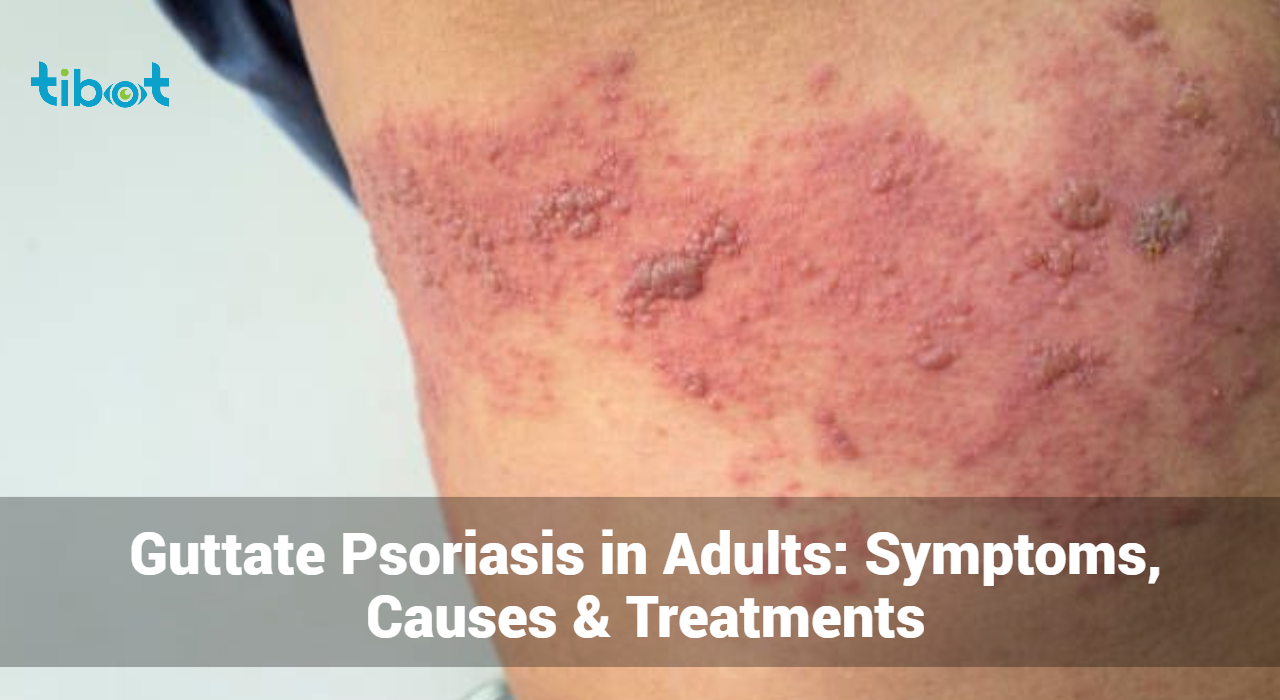
Guttate psoriasis is characterized by small, drop-shaped lesions that typically appear on the trunk, arms, legs, and scalp. The term “guttate” is derived from the Latin word “gutta,” meaning “drop,” which aptly describes the appearance of the lesions. Unlike other forms of psoriasis, guttate psoriasis often develops suddenly, frequently following a streptococcal throat infection.
What The Symptoms of Guttate Psoriasis?
The symptoms of guttate psoriasis can vary from person to person, but common signs include:
- Small, Red Spots: These lesions are usually less than one centimeter in diameter and can appear in clusters.
- Scaling: The spots are often covered with fine, silvery scales that may flake off.
- Itching and Irritation: Many individuals experience itching, which can lead to discomfort and scratching.
- Dry Skin: The affected areas may become dry and cracked.
- Nail Changes: Some individuals may notice pitting or other changes in their nails.
What Causes of Guttate Psoriasis?
While the exact cause of guttate psoriasis is not fully understood, several factors are believed to contribute to its development:
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of psoriasis can increase the likelihood of developing guttate psoriasis.
- Infections: Streptococcal infections, particularly strep throat, are commonly associated with the onset of guttate psoriasis.
- Environmental Triggers: Factors such as stress, skin injuries, and certain medications can trigger or exacerbate symptoms.
- Immune System Dysfunction: Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition, meaning the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to rapid skin cell turnover and inflammation.
How is guttate psoriasis diagnosed?
-
Medical History: The healthcare provider will ask about the patient’s symptoms, family history of psoriasis or other skin conditions, and any recent infections or illnesses that may have triggered the flare-up.
-
Physical Examination: The doctor will examine the skin for the characteristic small, drop-shaped lesions that are typical of guttate psoriasis. These lesions often appear on the trunk, arms, legs, and scalp.
-
Skin Biopsy: In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to rule out other skin conditions and confirm the diagnosis. The biopsy involves taking a small sample of skin tissue for laboratory analysis.
-
Assessment of Triggers: The doctor may also assess potential triggers, such as recent streptococcal infections, stress, or certain medications, which can contribute to the onset of guttate psoriasis.
It’s important for individuals experiencing symptoms to consult a dermatologist healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Analyze Skin Diseases
Use our AI chatbot to determine your skin condition
What Are The Treatment Options for Guttate Psoriasis?
Treatment for guttate psoriasis aims to reduce symptoms, clear the skin, and prevent flare-ups. Options include:
1. Topical Treatments
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory creams or ointments can help reduce redness and itching
-
Vitamin D Analogues: These topical treatments, such as calcipotriene, help slow down skin cell growth and can be effective in managing psoriasis.
-
Retinoids: Topical retinoids, like tazarotene, can help reduce inflammation and normalize skin cell production.
-
Coal Tar: This traditional treatment can help reduce scaling, itching, and inflammation.
2. Phototherapy
-
Ultraviolet B (UVB) Therapy: This treatment involves exposing the skin to UVB light, which can help reduce symptoms and clear lesions.
-
Psoralen plus Ultraviolet A (PUVA): This combination therapy involves taking a medication called psoralen before exposure to UVA light, which can be effective for more severe cases.
3. Systemic Treatments
For moderate to severe guttate psoriasis, systemic treatments may be necessary. These include:
-
Oral Medications: Drugs such as methotrexate, acitretin, or cyclosporine can help control the immune response and reduce symptoms.
-
Biologics: These are newer medications that target specific parts of the immune system. They are typically used for moderate to severe psoriasis and may be administered via injection or infusion.
4. Lifestyle and Home Remedies
-
Moisturizers: Keeping the skin well-hydrated can help reduce dryness and scaling.
-
Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers such as stress, infections, or certain medications can help prevent flare-ups.
-
Healthy Diet: Maintaining a balanced diet and staying hydrated may support overall skin health.
Can guttate psoriasis be prevented?
-
Manage Infections: Since guttate psoriasis can be triggered by infections, particularly streptococcal throat infections, maintaining good hygiene and seeking prompt treatment for infections can help.
-
Stress Management: Stress is a known trigger for psoriasis. Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or meditation may help minimize flare-ups.
-
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to overall skin health and potentially reduce the risk of flare-ups.
-
Skin Care: Keeping the skin moisturized and avoiding harsh soaps or irritants can help maintain skin integrity and reduce irritation.
-
Medication Awareness: Being aware of medications that may trigger psoriasis and discussing alternatives with a healthcare provider can be beneficial.
-
Regular Check-ups: Regular consultations with a dermatologist can help monitor the condition and adjust treatment as necessary.
While these strategies may help reduce the likelihood of developing guttate psoriasis or experiencing flare-ups, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and management.
Conclusion
Guttate psoriasis can be effectively managed with a combination of treatments tailored to the individual’s needs. It’s essential to work closely with consult a dermatologist or healthcare provider to determine the best approach and monitor the condition over time. Regular follow-ups can help adjust treatment as needed and ensure optimal management of symptoms.