Hidradenitis Suppurativa Pictures, Types, Causes, Symptoms and Treatments

Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by painful nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts in areas of the body where skin rubs together. These areas typically include the armpits, groin, buttocks, and under the breasts. HS is a debilitating condition that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life due to pain, scarring, and the psychological effects of dealing with a chronic illness. This article provides an in-depth look at HS, including visual representations, types, causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What is Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is a chronic, inflammatory skin condition that primarily affects areas of the body where skin rubs together, such as the armpits, groin, buttocks, and under the breasts. It is characterized by the recurrent formation of painful nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts (tunnel-like structures under the skin), which can lead to significant scarring and disfigurement over time.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa is a challenging and often painful condition that requires a comprehensive approach to management. Early diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and lifestyle modifications can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. Consulting a dermatologist for ongoing care and support is crucial for effectively managing this chronic skin condition.
Different Types of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is typically classified based on the severity and extent of the disease using the Hurley staging system. This system helps healthcare providers determine the appropriate treatment plan for each patient. Here’s a detailed look at the different types of HS according to the Hurley staging system:
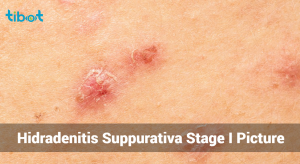
Hurley Stage I:
- Characteristics:
Isolated inflamed nodules that resemble boils. These may resolve without treatment or progress to abscess formation.
-
- Single or multiple isolated abscesses.
- No sinus tracts (tunnels under the skin) or scarring.
- Lesions may heal on their own or with minor treatment.
- Symptoms:
- Painful, red lumps or nodules, often mistaken for boils.
- Abscesses that may be tender and filled with pus.
- Treatment:
- Topical antibiotics (e.g., clindamycin) to reduce inflammation.
- Warm compresses to alleviate pain and encourage drainage.
- Good hygiene practices to prevent further infection.
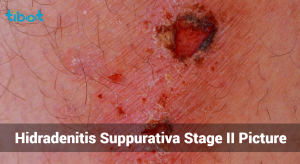
Hurley Stage II:
- Characteristics:
Recurrent abscesses that can lead to the formation of sinus tracts and scarring. The lesions are more widespread, but they are still relatively isolated.
-
- Recurrent abscesses with sinus tract formation.
- Moderate scarring between lesions.
- More widespread lesions, but still relatively isolated.
- Symptoms:
- Painful, swollen lumps that may burst and release pus.
- Formation of tunnels under the skin connecting abscesses.
- Moderate scarring and thickening of the skin.
- Treatment:
- Oral antibiotics (e.g., tetracycline, doxycycline) to control infection and inflammation.
- Intralesional corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and shrink nodules.
- Laser therapy to remove affected tissue and reduce recurrence.
- Weight management and smoking cessation to reduce risk factors.
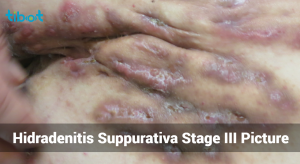
Hurley Stage III:
- Characteristics:
Multiple interconnected sinus tracts and abscesses across large areas of the body. The skin may become thickened and scarred.
-
- Diffuse or broad involvement across large areas of the body.
- Multiple interconnected sinus tracts and abscesses.
- Extensive scarring and chronic inflammation.
- Symptoms:
- Large, painful abscesses that rupture and drain.
- Significant scarring and skin thickening.
- Extensive sinus tract networks under the skin, leading to chronic infection.
- Treatment:
- Biologic therapies (e.g., TNF inhibitors like adalimumab) to target immune response.
- Wide surgical excision to remove affected areas and sinus tracts.
- Skin grafting or reconstruction following extensive surgical removal.
- Ongoing management with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications.
- Psychological support to address the emotional and mental impact of severe HS.
What Are The Causes of Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
The exact cause of HS is not fully understood, but several factors are thought to contribute to its development:
- Genetic Factors:
- Family history of HS increases the risk of developing the condition, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
- Hormonal Changes:
- HS often begins after puberty and can fluctuate with menstrual cycles, indicating a hormonal influence.
- Immune System Dysfunction:
- HS is believed to involve an abnormal response of the immune system, leading to chronic inflammation.
- Lifestyle Factors:
- Smoking and obesity are associated with a higher risk and severity of HS. These factors can exacerbate the condition by promoting inflammation and mechanical stress on the skin.
- Friction and Sweat:
- Areas of the body where skin rubs together and where sweat glands are abundant are more prone to HS. Friction and moisture can irritate the skin and promote bacterial growth, leading to infection and inflammation.
Symptoms of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
HS symptoms can vary in severity and presentation. Common symptoms include:
- Painful, Pea-sized Lumps or Nodules:
- These lumps can develop in areas such as the armpits, groin, buttocks, and under the breasts. They may be tender to the touch and can grow in size.
- Abscesses:
- Abscesses filled with pus may develop and rupture, causing pain and discharge. This can lead to unpleasant odors and drainage.
- Sinus Tracts:
- Chronic HS can result in the formation of sinus tracts, which are tunnel-like connections between abscesses under the skin. These tracts can be painful and lead to further infection.
- Scarring:
- Recurrent inflammation and abscesses can lead to significant scarring and thickening of the skin. Over time, this can cause restricted movement and further discomfort.
- Blackheads:
- Comedones, or blackheads, may form in the affected areas, often appearing in pairs or in clusters.
- Itching and Burning:
- The affected areas may be itchy and have a burning sensation due to inflammation and infection.
What Are The Treatments for Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
Treatment for HS aims to manage symptoms, prevent flare-ups, and improve the quality of life. The treatment approach varies depending on the severity of the condition:
Analyze Skin Diseases
Use our AI chatbot to determine your skin condition
- Topical Treatments:
- Topical Antibiotics:
- Clindamycin is commonly used to reduce inflammation and bacterial infection in mild cases of HS.
- Topical Retinoids:
- These can help to normalize skin cell turnover and reduce clogging of hair follicles.
- Topical Antibiotics:
- Oral Medications:
- Antibiotics:
- Long-term antibiotics such as tetracycline, doxycycline, or minocycline can help control symptoms and reduce inflammation. They are often used for moderate to severe cases.
- Hormonal Therapy:
- Birth control pills or anti-androgen medications, such as spironolactone, can be effective in women by reducing hormonal triggers of HS.
- Retinoids:
- Oral retinoids, such as isotretinoin, may be prescribed for severe cases. These medications can reduce sebaceous gland activity and normalize skin cell production.
- Biologics:
- TNF inhibitors, such as adalimumab, can help reduce inflammation in moderate to severe cases of HS. These medications target specific pathways in the immune system that contribute to inflammation.
- Immunosuppressants:
- Medications such as methotrexate or cyclosporine can help manage severe inflammation by suppressing the immune system.
- Antibiotics:
- Surgical Treatments:
- Incision and Drainage:
- This procedure can relieve pain and pressure from abscesses by draining the pus. However, it is a temporary solution and does not prevent recurrence.
- Laser Therapy:
- CO2 laser can remove affected tissue and reduce the recurrence of lesions. It is effective for localized disease.
- Excision:
- Surgical removal of affected skin areas and sinus tracts may be necessary in severe cases. This can help to reduce symptoms and prevent recurrence. Wide excision can be more definitive, but it may also involve a longer recovery time.
- Punch Debridement:
- This procedure involves removing small areas of skin affected by HS using a circular blade. It is less invasive than wide excision and can be effective for isolated lesions.
- Incision and Drainage:
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Weight Management:
- Reducing body weight can help decrease symptoms of HS by reducing friction and pressure on affected areas.
- Quit Smoking:
- Smoking cessation can improve HS symptoms and overall health. Smoking is known to exacerbate inflammation and may worsen HS.
- Hygiene Practices:
- Keeping affected areas clean and dry can help prevent infection and reduce irritation. Gentle cleansing with non-irritating soaps and avoiding harsh scrubbing can be beneficial.
- Dietary Changes:
- Some patients find relief by avoiding foods that trigger inflammation, such as dairy, sugar, and processed foods. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, may help manage symptoms.
- Weight Management:
- Home Care:
- Warm Compresses:
- Applying warm compresses to affected areas can help reduce pain and swelling. It can also encourage drainage of abscesses.
- Loose Clothing:
- Wearing loose, breathable clothing can minimize friction and irritation on affected areas. Choosing fabrics like cotton can help keep the skin dry and reduce sweat buildup.
- Anti-inflammatory Supplements:
- Supplements such as turmeric, which has anti-inflammatory properties, may help reduce inflammation in some patients. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
- Warm Compresses:
- Psychological Support:
- Counseling:
- Living with a chronic condition like HS can take a toll on mental health. Counseling or therapy can help patients cope with the emotional and psychological challenges of the disease.
- Support Groups:
- Joining support groups, either in-person or online, can provide a sense of community and support. Sharing experiences and tips with others who have HS can be empowering.
- Counseling:
How Can Hidradenitis Suppurativa Prevention and Management Tips?
- Early Intervention:
- Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the progression of HS and reduce the risk of complications. Seek medical advice at the first sign of symptoms.
- Identify Triggers:
- Keeping a symptom diary can help identify triggers such as certain foods, stress, or hormonal changes. Avoiding these triggers can help manage flare-ups.
- Consistent Skincare Routine:
- Maintaining a consistent skincare routine that includes gentle cleansing and moisturizing can help keep the skin healthy and reduce irritation.
- Regular Follow-up:
- Regular follow-up appointments with a dermatologist are important for monitoring the condition and adjusting treatment plans as needed.
Conclusion
Hidradenitis Suppurativa is a challenging and often painful condition that requires a comprehensive approach to treatment and management. Understanding the different types, causes, symptoms, and available treatments can empower patients to take control of their condition and improve their quality of life. While there is no cure for HS, effective management strategies and lifestyle changes